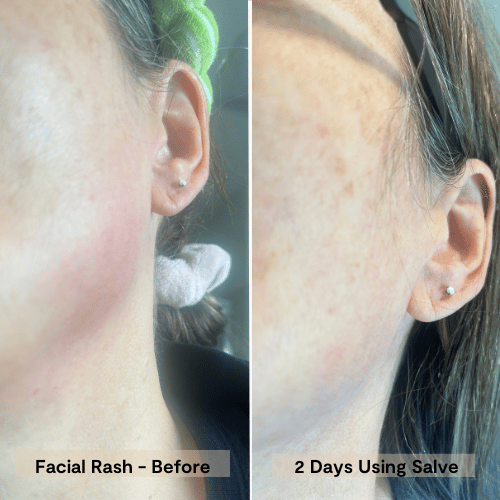
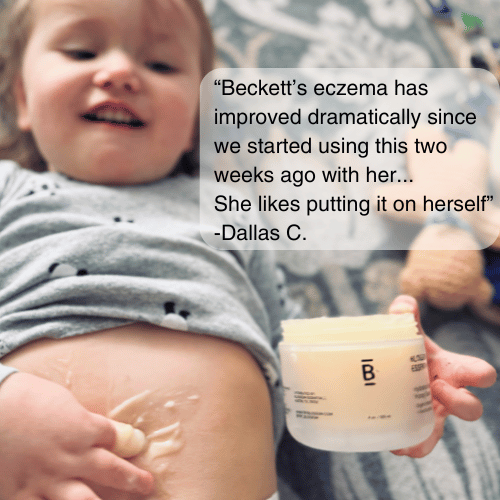
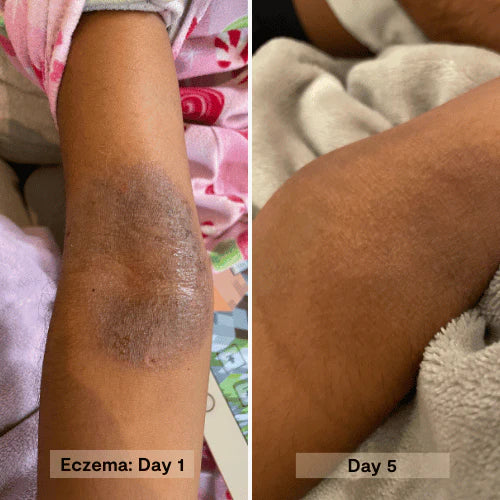
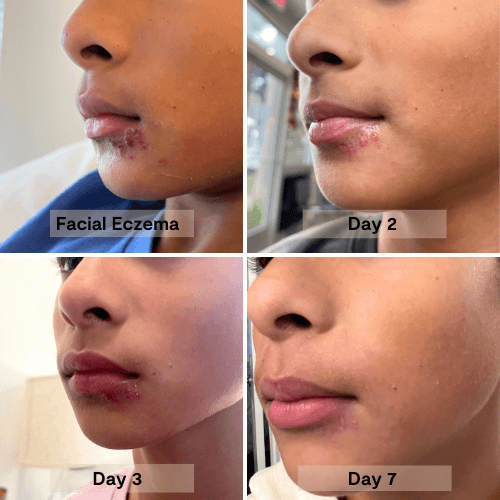
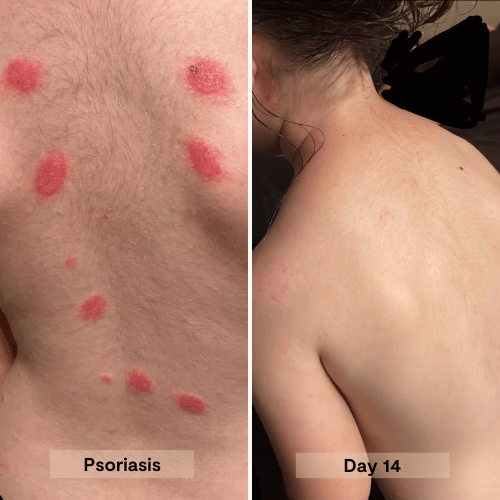
A potent blend of organic Manuka honey, nourishing oils, and natural moisturizers penetrates deeply to intensely hydrate, relieve dryness, and repair the skin barrier. This salve quickly soothes damaged, itchy skin, leaving it rejuvenated, healthy, and wonderfully soft.
SWEET RELIEF: THE ROLE OF HONEY IN SOOTHING ECZEMA
Honey, nature’s golden elixir, is known to soothe eczema’s itch and inflammation. Here, we look at its history, effectiveness, and types, offering practical tips for integrating honey into your skincare routine. Uncover myths and truths about honey’s healing powers, and find answers to common questions about this sweet remedy.
THE HISTORY OF HONEY AND ECZEMA
Honey, often hailed as nature's golden elixir, has been cherished for centuries not only for its sweet taste but also for its myriad of health benefits. Among its many uses, honey has gained attention for its potential in soothing eczema, a common skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed patches. Eczema affects millions worldwide, and while there is no definitive cure, managing its symptoms is key to improving quality of life. Honey's natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising candidate for alleviating eczema symptoms. But how exactly does it work, and is it truly effective? Let's dive into the sticky details.
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition that can be triggered by various factors, including allergens, irritants, and even stress. The quest for relief often leads individuals to explore both conventional treatments and natural remedies. Honey, with its rich history in traditional medicine, has emerged as a popular choice. Its ability to retain moisture and promote healing makes it an appealing option for those seeking a natural approach to skincare. However, while honey's potential benefits are enticing, it's essential to understand its limitations and how it fits into a comprehensive eczema management plan. As we explore honey's role in eczema care, we'll uncover the science behind its soothing properties and offer practical tips for incorporating it into your skincare routine.

WHY IS HONEY AN ECZEMA BEATER?
Honey's effectiveness in treating eczema lies in its natural properties that make it a powerful ally against skin irritation and inflammation. At the heart of honey's therapeutic potential is its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory nature. Honey contains hydrogen peroxide, a natural antiseptic, which helps cleanse the skin and prevent infection in eczema-prone areas. Additionally, honey's high sugar content creates an environment that is inhospitable to bacteria, further reducing the risk of infection. The anti-inflammatory properties of honey help to soothe the skin, reducing redness and swelling, which are common symptoms of eczema. This dual action of fighting bacteria and calming inflammation makes honey a versatile remedy for those seeking relief from eczema flare-ups.
Moreover, honey is a natural humectant, meaning it has the ability to attract and retain moisture. This is particularly beneficial for eczema sufferers, as dry skin can exacerbate symptoms and lead to further irritation. By locking in moisture, honey helps maintain the skin's natural barrier, promoting healing and preventing further damage. Manuka honey, in particular, is renowned for its unique antibacterial properties due to the presence of methylglyoxal (MGO), making it a popular choice for eczema treatment. While honey is not a cure for eczema, its ability to hydrate, protect, and heal the skin makes it a valuable component of a holistic skincare regimen aimed at managing this chronic condition.

WILL ANY HONEY WORK ON ECZEMA?
When it comes to using honey for eczema, not all honey is created equal. The type of honey you choose can significantly impact its effectiveness in soothing eczema symptoms. Manuka honey, for instance, is often hailed as the gold standard due to its unique antibacterial properties. Originating from New Zealand, Manuka honey contains high levels of methylglyoxal (MGO), which gives it potent antimicrobial effects. This makes it particularly effective in reducing infection risk and promoting healing in eczema-affected areas. Its thick, viscous texture also helps create a protective barrier on the skin, locking in moisture and providing relief from dryness and irritation.
On the other hand, ultra-processed honey with added sugars is not recommended for eczema treatment. This type of honey often undergoes extensive processing, stripping away many of its natural beneficial properties. The addition of sugars and other additives can further dilute its effectiveness, making it less suitable for therapeutic use. When selecting honey for eczema, it's crucial to opt for raw or minimally processed varieties. These types of honey retain more of their natural enzymes and nutrients, which are essential for their healing properties. Look for labels that indicate the honey is raw, unfiltered, and free from additives to ensure you're getting the most benefit.
Beyond Manuka and processed honey, there are other varieties worth considering. Raw honey, for instance, is a great alternative for those who may not have access to Manuka honey. It retains its natural enzymes and nutrients, offering antibacterial and moisturizing benefits similar to Manuka honey, albeit to a lesser extent. Buckwheat honey is another option, known for its high antioxidant content, which can help reduce inflammation and promote skin healing. When choosing honey for eczema, it's essential to consider its purity, origin, and processing method to ensure you're using a product that will effectively soothe and heal your skin.

HOW TO APPLY HONEY
Incorporating honey into your eczema skincare routine can be both simple and effective, offering a natural way to soothe and heal your skin. One of the easiest methods is to apply raw or Manuka honey directly to the affected areas. Simply spread a thin layer over the eczema patches, let it sit for about 20-30 minutes, and then rinse off with warm water. This can be done once or twice daily to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
For those who prefer a more integrated approach, honey can be combined with other natural ingredients to create soothing masks or balms. Mixing honey with ingredients like aloe vera gel or coconut oil can enhance its moisturizing properties, providing additional relief from dryness and irritation. Apply the mixture to the skin, leave it on for a while, and then gently wash it off. This combination not only hydrates but also forms a protective barrier on the skin, aiding in the healing process.
If you prefer over-the-counter products, look for creams and lotions that contain honey as a key ingredient. These products often combine honey with other beneficial compounds to enhance its effects. When selecting such products, ensure they are free from harsh chemicals and fragrances that could aggravate eczema. Incorporating honey into your daily skincare routine, whether through direct application or as part of a product, can be a sweet solution to managing eczema symptoms.
Aging Skin Mythbusting
Truth: While honey can help soothe and manage eczema symptoms, it is not a cure. Eczema is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and care.
Truth: Not all honey is created equal. Raw and Manuka honey are more effective due to their natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, while processed honey with added sugars may not offer the same benefits.
Truth: While honey is naturally sticky, applying a thin layer and rinsing it off after a short period can minimize mess and still provide benefits to the skin.
Truth: Honey is generally gentle and soothing, but it's always a good idea to perform a patch test first, especially for those with sensitive skin, to ensure there is no adverse reaction.
Truth: Eczema is not contagious. It is a skin condition caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, and it cannot be spread from person to person.
Truth: Like many natural remedies, honey may take time to show its full effects. Consistent use over time can help manage symptoms more effectively.

THE HONEY-ECZEMA LOWDOWN
Honey, with its rich history and natural healing properties, offers a promising avenue for those seeking relief from eczema's persistent symptoms. While it is not a cure, honey's antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and moisturizing qualities make it a valuable addition to a comprehensive skincare routine. Whether you choose Manuka honey for its potent effects or opt for raw honey as a more accessible alternative, incorporating this sweet remedy can help soothe irritation and support skin healing. It's essential to remember that consistency is key, and while results may not be immediate, regular use can lead to noticeable improvements over time.
As you explore the potential of honey in managing eczema, it's crucial to remain informed and discerning. Not all honey is created equal, and selecting the right type can significantly impact its effectiveness. By understanding the differences between honey varieties and debunking common myths, you can make informed decisions that align with your skincare goals. Whether through direct application or as part of a product, honey can be a sweet solution to the challenges of eczema, offering a natural path to healthier, more comfortable skin.

Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, honey is generally safe for eczema-prone skin, but it's always recommended to perform a patch test first to ensure there are no adverse reactions.
You can apply honey once or twice daily, depending on your skin's tolerance and the severity of your symptoms.
It's best to use raw or Manuka honey, as they retain more natural enzymes and nutrients beneficial for eczema, unlike processed honey with added sugars.
Results can vary, but consistent use over several weeks is often needed to notice significant improvements.
Yes, honey can complement other treatments, but it's important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure compatibility.
Honey is naturally sticky, but applying a thin layer and rinsing it off after a short period can minimize any mess.
Manuka honey is often preferred due to its unique antibacterial properties, making it more effective for some individuals.
Honey can be used for children, but it's essential to consult a pediatrician first, especially for children under one year old, due to the risk of botulism.